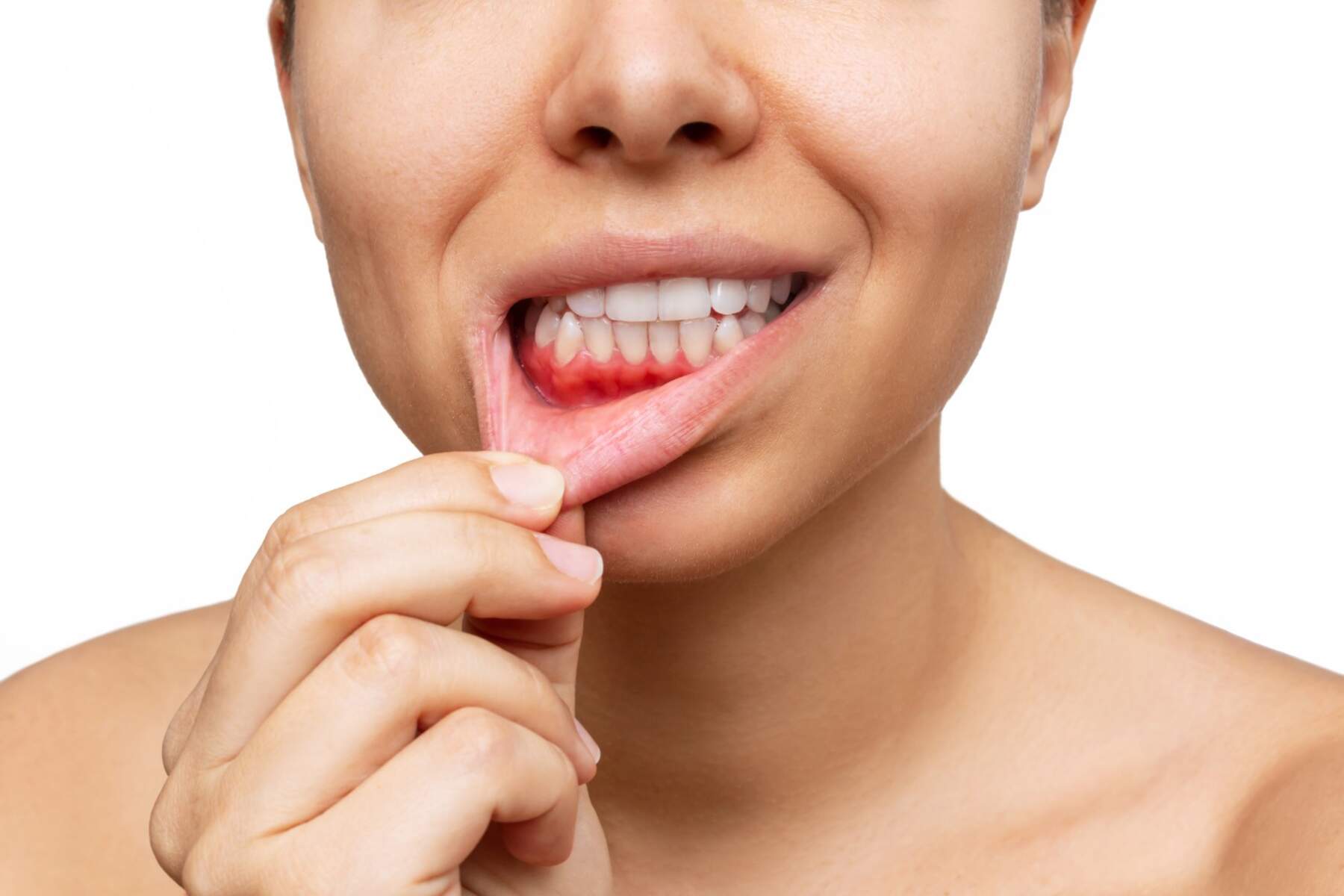
Taking care of your gums is very important for maintaining your oral health. The gingiva is the hard pink tissue that covers the jawbone. This tissue is thick, fibrous, and full of blood vessels. Swollen gums may protrude, bleed or swell. Swollen gums usually start where the gums meet the teeth. However, sometimes the gums are so swollen that they cover part of the tooth and they appear red instead of their usual pink color. After brushing and flossing your teeth your gums may bleed or swell more easily. In this article we will talk about everything you need to know about the causes and treatment for swollen or bleeding gums.
What are bleeding gums?
Bleeding gums are the most common symptom of gum disease. But it can also point to other health problems.
Occasional bleeding of the gums can be caused by brushing your teeth too vigorously or wearing dentures that don’t fit correctly. Frequent gum bleeding can also indicate more serious conditions, including:
- periodontitis (an advanced form of gum disease)
- leukemia (cancer of the blood)
- vitamin deficiency
- lack of clotting cells (platelets)
Dental conditions that can cause bleeding gums
Dental health problems are the main cause of bleeding gums. Gingivitis (inflammation of the gums) and periodontitis can make your gums sensitive and prone to bleeding.
Gingivitis
Most people develop gingivitis when plaque remains in the gum line for too long. Plaque is the dirt and bacteria that sticks to your teeth. Brushing your teeth removes plaque and prevents tooth decay. However, without proper brushing and flossing, plaque can remain on the gum line.
If plaque is not removed, it can harden into tartar (tartar) and cause more bleeding. Plaque buildup near the gums can also cause gingivitis.
Symptoms of gingivitis include:
- puffy gums
- soreness in the mouth and around the gums
- bleeding gums
Periodontitis
As gingivitis progresses, it can lead to periodontal disease (periodontal disease). Periodontitis is an infection of the gums, jawbone, and supporting tissues that connect the teeth to the gums. Gum disease can cause teeth to become loose or fall out.
Vitamin deficiency
A lack of vitamin C or vitamin K can make your gums bleed more easily.
If you have bleeding gums that aren’t caused by poor dental care, ask your doctor to check your vitamin C and K levels. Also, follow a diet that includes both nutrients to ensure you’re getting the vitamins you need to stay healthy.
Foods rich in vitamin C include:
- citrus fruits and juices
- broccoli
- strawberries
- tomatoes
- potatoes
- bell peppers
Foods rich in vitamin K include:
- watercress
- kale
- spinach
- Swiss chard
- lettuce
- mustard greens
- soybeans
- canola oil
- olive oil
Other causes of bleeding gums
People with dentures can also suffer from bleeding gums. This is more likely to happen if your dentures are too tight.
If your dentures or other braces are causing bleeding gums, see your dentist or orthodontist. New impressions may need to be taken to create a more suitable mouthpiece.
Bleeding gums are also common during pregnancy. Hormonal changes during pregnancy can make your gums more sensitive.
Bleeding disorders such as hemophilia and leukemia can also increase the risk of bleeding gums. Taking blood-thinning medications can make your gums bleed more often. Drugs in this class include warfarin, aspirin, and heparin.
Treatment for bleeding gums
Making sure to practice good dental hygiene is the first step in treating bleeding gums.
Visit your dentist twice a year for a professional teeth cleaning. Your dentist can tell you if you have gingivitis and teach you how to brush your teeth correctly. Proper brushing and flossing removes plaque from the gum line and reduces the risk of periodontitis. Your dentist can also teach you how to use antiseptic mouthwash to minimize plaque buildup in your mouth. Also, rinsing with warm salt water can help soothe swollen gums that bleed easily.
Use a soft toothbrush which is gentle on inflamed gums, especially if you experience bleeding after brushing your teeth. You can also use an electric toothbrush. The specially designed brush heads on these toothbrushes help clean the gum line more easily than manual toothbrushes.
What causes swollen gums?
Swollen gums are often caused by gingivitis, but can be caused by many other factors, including pregnancy, malnutrition, and certain types of infections.
Gingivitis
Gingivitis is the most common cause of swollen gums. Many people are unaware that they have gingivitis because the symptoms are so mild. However, if left untreated, gingivitis can eventually lead to a much more serious condition called periodontitis, which can lead to tooth loss.
Gingivitis most often results due to poor oral hygiene that causes plaque to build up on the gum lines and teeth. Plaque is a film of bacteria and food debris that builds up on teeth over time. If plaque remains on your teeth for more than a few days, it becomes tartar. Tartar is a hardened plaque that cannot be removed by flossing or brushing alone. In this case, you should see a dentist, as tartar formation can lead to inflammation of the gums.
Pregnancy
Pregnancy can also be a cause for swollen gums. The increase in hormones produced by your body during pregnancy may increase the blood flow in your gums. Consequently, the increase in blood flow can cause your gums to be more easily irritated, leading to swelling.
These hormonal changes can also reduce your body’s ability to take care of the bacteria that usually causes gum infections. In turn this can increase your chances of developing gingivitis.
Malnutrition
Vitamin deficiency, especially vitamin B and C, can cause gum swelling. Vitamin C, for example, is crucial when it comes to the maintenance and repair of your teeth and gums. If your vitamin C levels decrease too much, you could develop scurvy which can cause anemia and gum disease.
Infections
Infections due to fungi and viruses can be a potential cause of swollen gums. For example, if you have herpes, it could lead to a condition called acute herpetic gingivostomatitis, which in turn causes your gums to swell.
Thrush, a condition which results from an overgrowth of naturally occurring yeast in the mouth, can also cause gum swelling. Moreover, any untreated dental decay issues can result in dental abscess. Dental abscess is localized gum swelling which requires treatment from a dentist.
What are the treatment options for swollen gums?
Medical treatment
If your gums have been swollen for more than two weeks, see your dentist. The dentist will ask when and how often symptoms started.
A full oral dental x-ray may be required to confirm bone loss. They will also want to know if you are pregnant or if you have recently changed your diet. They may order blood tests to check for infection. Depending on the cause of swollen gums, your dentist may prescribe a mouthwash to help prevent gingivitis and reduce plaque. They may also recommend using a particular brand of toothpaste. In some cases, antibiotics may be required.
Severe gingivitis may require surgery. This is usually only recommended for people with late stage periodontal disease, including moderate or advanced periodontitis. Common treatment options are scaling and root planing. This is a procedure where the dentist scrapes off the diseased gums, plaque, and tartar at the base of the tooth, allowing the remaining gums to heal.
At-home treatments
You should make sure to treat swollen gums with care. A few tips for at-home care include:
- Brush your teeth gently so as not to irritate your gums.
- Rinse your mouth with salt water to remove bacteria in your mouth.
- Drink lots of water. Water stimulates the production of saliva and weakens disease-causing bacteria in the mouth.
- Avoid irritants such as strong mouthwash, alcohol, and tobacco.
- Apply a warm compress to your face to help relieve gum pain.
- Cold compresses can help reduce swelling.
How can I prevent swollen gums?
Here are some of the preventive measures you can take to avoid swollen gums, including properly taking care of your health and eating healthy foods.
Oral health care
Make sure to brush and floss regularly, especially after meals. See a dentist at least once every 6 months for professional cleaning and discuss any other symptoms and issues you may be experiencing. For example, if you have dry mouth, a problem often caused by certain health issues or medications, it can increase the risk of plaque and tartar building up. You can also discuss with a dentist about mouthwash and toothpaste alternatives that can help with maintaining proper gum health.
Reducing your stress levels
Some studies suggest that chronic stress may be associated with an increased risk of periodontal disease. Not only that, stress can aggravate gum problems and make treatment less effective.Controlling stress levels can help prevent swollen gums and improve oral health. Yoga, meditation and deep breathing exercises are simple and effective ways to reduce stress.
Use toothpaste for gum health
Different types of toothpaste contain ingredients that help improve oral health by reducing tooth sensitivity, relieving gingivitis, reducing tartar build-up, or preventing enamel erosion. It is recommended to choose a toothpaste that contains fluoride and is free of sugar and other flavors that can cause cavities. To keep your gums healthy, brush your teeth regularly twice a day with toothpaste and floss.
While bleeding and swollen gums are one the most common symptoms of dental problems, there are other factors which can contribute to their cause. Book an appointment with your dental care specialist to determine whether dental health is the main issue causing your bleeding or swollen gums. A physical examination and blood tests can help identify the cause of your bleeding and swelling. Proper treatment will vary according to your condition, but it is always advised to seek help as soon as possible for better results.