Ouch! You bite into a crunchy apple. You take a sip of iced water and ack! Or perhaps you’re doing absolutely nothing and everything when — zap! — toothache hits randomly.
Whether it just occurs while the teeth are in use or you can’t manage to get rid of the core soreness, tooth pain requires your care and concern. Because your oral health affects your general health, tooth pain may be attempting to inform you of anything.
But what could it possibly be? Below, we will present you with the reasons behind toothache and how to get them solved in Albania.
Cavities
A cavity occurs whenever the tooth enamel dwindles, resulting in a little hole in the tooth. When one cavity is detected early (say, for instance, following the annual dentist visit), it is generally possible to treat it prior to the pain it causes. Multiple cavities, on the other hand, can be agonizing and destructive. Once cavities become serious and adjacent to the nerve, they can produce substantial discomfort and necessitate consulting with a dentist or an endodontist, known in other words as a “root canal expert,” so he or she can perform a root canal. In other situations, the tooth might even need to be extracted.
You’re exercising excessively.
Though regular exercise can be beneficial to both the body and the mind, exercising excessively may be the source of the toothache. Research has discovered that marathoners who engage in intense exercise have a greater chance of tooth erosion than those who do not exercise. The lack of saliva during exercise can cause a lack of enamel on the teeth.
A Filling Broke
The filling material deteriorates, and the dental filling might fall out if excessive pressure is applied to the site. Another reason behind the broken filling can also happen due to decay surrounding or beneath a filling. Many people might not notice anything is wrong until they chomp down. When they chew, a break in the filling might allow the food to get shoved into the site, causing discomfort and pain.
You’ve got an abscess
As nutrients become lodged within the teeth and the chewing continues, the food moves further into the gums. These remaining trash particles degrade over time, promoting this illness. The earlier the infection is cured, the better, because an infected abscess can progress to gum disease.
A Broken Tooth
A toothache can be caused by a fracture or crack in the tooth. A tiny break, typically induced by chewing on anything hard, might cause discomfort whenever you chew or bite. Depending on the extent of the break, there might be a crown or an implant required to repair the badly broken tooth.
Wisdom Teeth Impairment
Wisdom teeth that try to erupt through the gums in a strange situation or with the insufficient room will cause tooth pain. Effected wisdom teeth pose a higher chance of uncomfortable infection or inflammation in the gums when they have pierced through the gum tissue. Affected teeth are difficult to access with a toothbrush or floss, posing this way a problem with proper oral care habits.
Sharp Ache
Any type of dental irritation must be evaluated by the dentist as soon as possible. Intense discomfort, on the other hand, may signal that the delicate internal parts of the tooth are revealed or contaminated. To avoid the spread of bacteria to neighboring teeth, it is crucial for an infectious tooth to be treated as promptly as possible.
Hypersensitivity
Whilst tooth hypersensitivity can be induced by a variety of factors, it can also signify the development of diseases such as gum disease or a dental abscess. Usually, the dentist is the one to diagnose the underlying reason for the hypersensitivity and prescribe the most successful care.
Discoloration or darkening
Did you realize that your teeth are somewhat translucent? If the tissue within the painful tooth becomes dark when compared to the teeth around it, the tissue might be significantly injured or infected. It is time to see an urgent dentist soon away if you want to save the tooth and save the teeth around that one.
Neck, jaw, or facial swelling
Infection is frequently accompanied by swelling. In the event that you have an infected tooth, the bacteria it contains will spread to the glands in your jaw and neck and cause their enlargement. Seek quick medical assistance if you detect puffiness, since the illness may migrate to other regions of your organism.
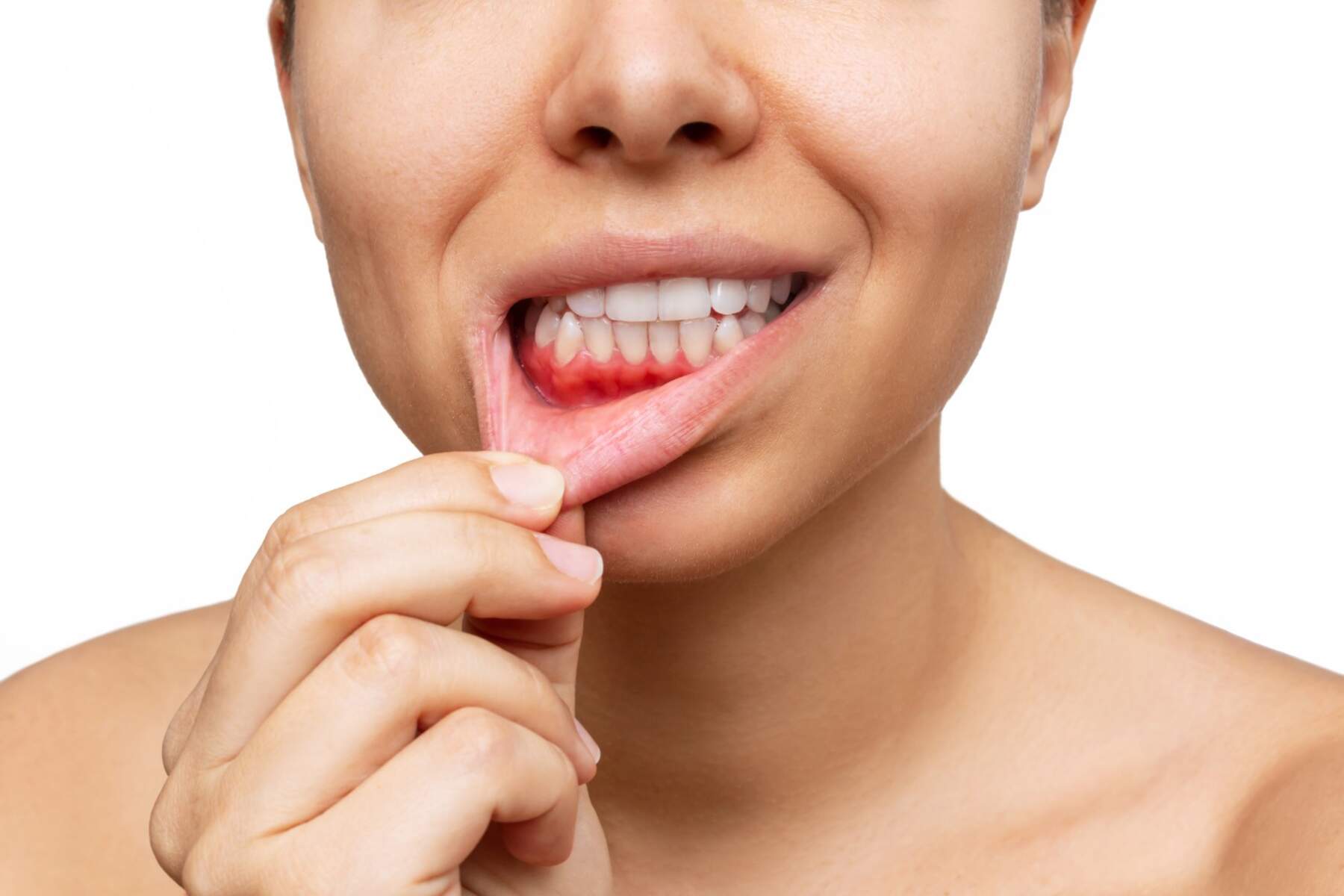
Gums that are puffy and bleed
Gums that are swollen and cause bleeding are early indicators of gum disease, a common affliction. Although keeping this bacterial infection untreated might result in irreversible harm, if discovered and diagnosed quickly enough, the early stages can be reversed.
Teeth that are loose
Gum disease, in its later phases, attacks the jaw and destroys the soft tissue that supports the teeth in their place. If you have a loosened lifelong tooth, it is at risk of falling out; therefore, a consultation with the dentist should be immediately booked to secure it and safeguard the remainder of the smile.
Chronic bad breath or a bad aftertaste
Toxins produced by germs in an infected tooth contaminate the odor and create a terrible flavor in the mouth. If you have a toothache with these indications, you must immediately visit a dentist to stop the infection.
If unclear still on whether the tooth pain you have, needs immediate dental attention, call your dentist regardless. He or she is capable of examining your case over the phone and assessing whether you require an immediate dental visit.
Discomfort that persists
It is normal to feel some soreness after a dental operation as the gums and the teeth heal and adjust to the change. On the other hand, the discomfort that persists could signal the shifting of the teeth, the impacting of the wisdom teeth, or the rot of the teeth. If a dentist is contacted right away once any of these symptoms are noticed, he or she will be able to rapidly evaluate and treat them.
Enduring a toothache is very often justifiable for people who have a busy schedule or are afraid of visiting the dentist. Yet, keep in mind that a dentist can offer you long-term pain management, the type of management you require prior to the problem worsening. So, as soon as you experience pain, schedule an appointment with a dentist to check the problem out.
Grinding your teeth (bruxism)
You would think you would know when you were grinding your teeth, but far too frequently, people do not—notably if it occurs while they are deep asleep. Teeth grinding, which might occur at any time during the day or when you are asleep at night, can cause jaw pain and tooth loss, as well as deteriorate the enamel of the teeth over time.
A dentist cannot stop you from grinding your teeth; however, he or she can help minimize the damage done. He or she can create a personalized sleep guard that will offer you a steady and solid bite and a lessening of the tightening of the jaw muscles. There are several steps to be taken to attempt to quit grinding your teeth.
Bruxism is one of the many temporomandibular joint disorders, which impact the jaw joints as well as the tendons and tissues that surround them. Some are as follows:
- acute trauma, such as a fractured or dislocated jaw.
- temporomandibular joint arthritis.
- displacement of the joints.
- malocclusion, often known as a “bad bite”.
Besides causing tooth damage, these problems can produce indications such as jaw pain, a common complaint, so it’s critical to consult with your dentist about therapy.
A tooth abscess
When hearing the term “abscess,”, you can almost always assume it to be followed by certain pain. When an infection occurs in any part of the body and creates a pocket of pus, that is when it takes the name “abscess.” So, in simpler words, an abscessed tooth is a pus-filled pocket that develops surrounding the tooth.
Tooth abscesses are classified into three types:
- gingival, or gum, disease.
- peripheral refers to the end of the tooth’s root.
- periodontal disease affects the bones or tissues around the tooth.
There’s no way to tell on your own what kind of tooth abscess you have. For that, you’ll need to see a dentist who can diagnose it and treat the underlying infection. Options include an incision to drain the pus, a root canal, or a tooth extraction.
Root bruising
Another cause hidden behind tooth pain can be root bruising, which is a split in the root of the tooth. Seeing as it occurs deep beyond the enamel of the teeth and the surface of the gums, this type of dental injury is quite difficult to detect. They are not visible to the dentist by simply taking a glance at the mouth.
The root bruising can be extremely unlikely to be visible, even when a two-dimensional X-ray is taken. In case your dentist suspects a root fracture, he or she will most likely refer you to an endodontist, one who is specialized in root canals and is able to examine both the tooth and perform certain tests.
Allergies or a sinus infection
Sinus infections can cause a variety of symptoms, including migraines, congested noses, and coughing. You may also add dental discomfort to the checklist.
Once the sinuses become inflamed, they might become clogged or loaded with liquids. This can place stress on the cheekbones and teeth, causing pain across your face.
What constitutes one of the most frequent causes of sinus infections? Periodic allergies are common, as you may have figured. Although the allergies may not result in a sinus infection (hopefully), they can still place stress on the maxillary sinus and, as a result, the remainder of your face.
Is it possible that you have gum disease?
Gum (or periodontal) disease refers to an inflammation of the gums that can worsen with time. However, it rarely causes dental pain.
Somewhat paradoxically, gum disease causes major oral pain. Regardless of how severe, it is rarely a source of discomfort that requires people to see their dentists or orthodontists right away.
However, there seem to be additional signs of gum disease, such as:
- poor breath.
- gums that are bleeding or inflamed.
- teeth that are hypersensitive.
When the dentist is visited twice a year, he or she can frequently identify and treat premature gum disease. However, it is also important to schedule an annual exam with a dentist.
Chronic periodontitis is commonly treated with a thorough cleaning, also known as scaling and root planing, in which the dentists sedate the patient and clear the tartar under the gums. Dentists will also diagnose and treat advanced gum disease.
When should you see your dentist?
If the pain you are feeling is moderate to severe, attempt to endure it for a while in order to see if it fades away by itself (even more so if you are allergic or you have a sinus infection). Try giving it about three weeks to see if the pain is acceptable and if you intend to attempt to ride it out. Contact your dentist if the pain has not resolved after that time.
Consult your dentist as soon as you notice any of the following symptoms:
- a rise in the intensity or frequency of your suffering.
- there may be swelling or bleeding.
- teeth that are cracked or loose.
It is critical to pay attention to your mouth and teeth for your well-being and enjoyment. It is rarely a bad idea to visit the dentist or periodontist!